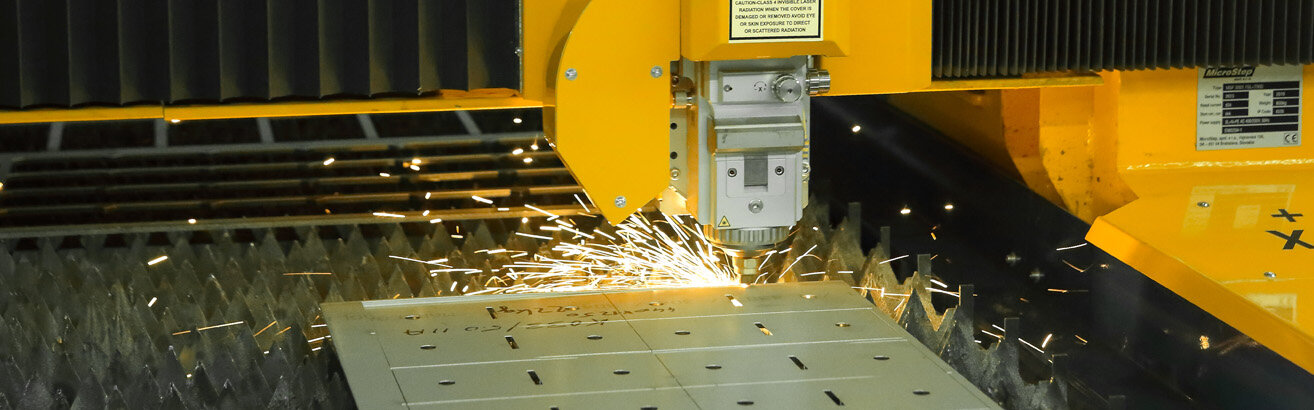
Laser cutting metal
Laser cutting systems are capable of cutting all typical metals used in industry. Alloys such as mild steel or stainless steel, non-ferrous metals such as aluminum or even precious metals can be processed with high quality. Thereby, laser cutting offers a number of advantages over other technologies for cutting metal. For example, very filigree and small contours can be cut from the material with high precision and speed.
What types of metal can be processed by laser?
In principle, all types of metal can be processed using CO2 and fiber laser technology. Due to the different absorption behavior of the laser wavelengths available today, not every laser type is equally suitable for every metal. For example, copper is much easier to cut with a fiber laser than with a CO2 laser. Depending on the grade, its material thickness, a possible alloy and the surface condition of the material, the cutting quality and speed varies depending on the technology and laser source strength used. Laser cutting systems are thus capable of cutting all typical metals used in industry. Whether it is alloys such as mild steel or stainless steel, non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, bronze, brass and copper, or precious metals such as gold, silver and platinum.
Advantages: Laser cutting of metal
- High accuracy
- Cutting of a wide range of materials
- Very high speed
- Contactless cutting process
- Wide range of applications
Examples of metal types
- Iron: Iron is the most commonly used metal in the world and, among other things, the main component of steel
- Aluminum: Aluminum is used as a substitute for iron, is significantly lighter but also more expensive, and is also very stable
- Copper: Copper has excellent electrical conductivity and is mainly used in electrical power lines
- Lithium: Lithium is considered the lightest of all metals and is an excellent store of electrons, making it ideal for batteries and rechargeable batteries
- Gold: Gold is one of the most expensive metals, is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity, is easy to work with, and is highly resistant to corrosion
- Platinum: Platinum is even more valuable than gold, is corrosion-resistant, flexible and easy to process
- Silver: Silver has excellent conductivity of electricity as well as heat, is flexible and ductile and – like gold – non-magnetic
What should be considered for laser cutting of metal?
Industrially used metals are very well suited for processing with the appropriate laser technology. Fiber laser technology in particular is capable of cutting a wide variety of metal types precisely, quickly and economically. For example, laser cutting of aluminum, copper or brass as well as mild steel and stainless steel is easily possible in various thickness ranges. The cutting quality depends to a large extent on the materials' characteristics. For example, material-specific properties such as alloying elements, microstructure or the material surface play a role here.
Advantages of laser technology for cutting metal
Laser cutting offers a number of advantages over other separation processes for metal. Laser cutting systems can cut out very filigree and small contours from the material with high precision and speed. The cut edges are very clean and therefore almost free of reworking, the heat-affected zone is very narrow and therefore the structural change is very small. The process is extremely flexible, with virtually no limits on the geometries to be cut. The technology shows its greatest strengths in sheet thicknesses of less than 10 mm, although the development of ever more powerful laser sources also enables economical cuts in increasing thicknesses.
Compared to plasma cutting and oxyfuel cutting, laser cutting scores points not only with speed and precision but also with a significantly lower heat input into the material. In contrast to waterjet cutting, laser cutting is many times faster. Compared to a punching machine, the laser is extremely economical even for small quantities, requires hardly any reworking and is significantly more flexible.
Where is laser cutting of metal used?
Laser cutting technology is used in numerous industries because of its diverse and flexible applications. Especially when high precision, high speeds, economic efficiency as well as flexibility in material processing are important and predominantly thinner material thicknesses are processed. This is the case as well in the automotive industry for the construction of prototypes or mass production as in plant engineering, facade construction, shipbuilding or the production of decorative elements such as in locksmith's shops.
Metal: What is this actually?
Anyone who remembers chemistry lessons and the periodic table of the elements will have a multitude of metals in mind. Around 80 percent of the elements found there are metals. We encounter iron, aluminum, copper, gold, silver and lead more or less visibly in everyday life. All substances found in nature share certain characteristics: metals have a high electrical conductivity that weakens with higher temperature, they have a strong thermal conductivity, are easy to form and shiny. They are used as pure materials or in alloys. In alloys, different metals are combined with other substances to bring their strengths together. Steel and structural steel are such compounds, which combine advantages such as strength or corrosion resistance, for example.
Laser cutting metal and bending
Once the sheets have been cut to size, they are usually bent. A combination of laser cutting system and press brake in your own company often forms a perfect duo. Among other things, the combination of both machines allows sheets to be processed in the press brake directly after laser cutting. This saves valuable time in the production process and enables a quick response to customer requirements.
You might also be interested in:
 SMART Cube X
SMART Cube X



 SmartLINE X
SmartLINE X
 MasterLINE X
MasterLINE X

 SMART Giant X
SMART Giant X
 TubeLINE
TubeLINE






 MSF Compact
MSF Compact

 MSF Cut
MSF Cut
 MSF Pro
MSF Pro


 MSF Max
MSF Max

 MasterCut Compact
MasterCut Compact
 MasterCut
MasterCut
 MG
MG

 DRM
DRM
 CombiCut
CombiCut
 DS
DS
 CPCut & PipeCut
CPCut & PipeCut
 ProfileCut
ProfileCut

 EasyCut
EasyCut

 WaterCut
WaterCut
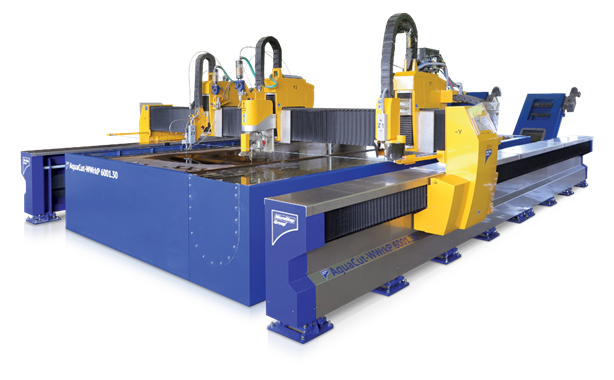
 AquaCut
AquaCut
 SMART
SMART

 eB ULTRA
eB ULTRA
 EUROMASTER
EUROMASTER
 GENIUS
GENIUS


 MSLoad, MSTower, MSSort
MSLoad, MSTower, MSSort



 MSLoop
MSLoop
 MSFeed
MSFeed
 Digitalization
Digitalization